Table of Contents
- What Is Generative Art?
- Objective of the Article
- How Generative Art Works
- Real-Life Examples of Generative Art in Marketing
- Advantages of Generative Art Integration
- Challenges of Generative Art Integration
- Statistical Insights into Generative Art Adoption
- Applications of Generative Art Across Fields
- Projections: Generative Art in the Future
- How Brands Can Leverage Generative Art
- The Canvas of Tomorrow
What Is Generative Art?
Generative art refers to art created autonomously by algorithms or AI systems. While the artist defines rules, constraints, and input parameters, the AI generates visuals, sound, or patterns based on these guidelines.
This blend of human creativity and machine efficiency is reshaping design across industries, offering new possibilities for advertising, social media, and general artistic expression.
With tools like DALL·E, MidJourney, and Runway, the integration of generative art into marketing and design has transitioned from mere imagination to an essential tool for creativity. The real question is not whether generative art can be integrated but how far it can push the boundaries of innovation.
Objective of the Article
- Define generative art and its applications.
- Highlight its integration into advertising, social media, and other fields.
- Analyze the benefits, challenges, and future potential.
How Generative Art Works

Generative art operates at the intersection of art and technology, leveraging machine learning (ML) models and neural networks to produce outputs based on a dataset of inputs.
For instance:
- An ad campaign might input brand colors, logos, and themes into AI to generate variations of digital posters.
- Social media managers use AI to create eye-catching visuals based on trending themes or holidays.
Real-Life Examples of Generative Art in Marketing
1. Coca-Cola: AI-Powered Design Contest
Coca-Cola launched a generative AI contest, inviting users to create AI-powered designs inspired by the brand. This campaign increased engagement while showcasing AI’s potential for creative collaboration.
2. Nike: Personalized Shoe Designs
Nike uses AI to let customers generate custom designs for shoes, blending personal creativity with brand identity.
3. Adidas: AI-Generated Campaigns
Adidas adopted generative AI to produce personalized advertisements, leveraging customer data to craft unique visuals that resonate with individual preferences.
Advantages of Generative Art Integration
1. Enhanced Creativity at Scale
- AI-generated designs provide limitless variations, enabling brands to experiment with unique concepts quickly.
2. Cost and Time Efficiency
- Automated art reduces the need for extensive manual work, saving resources.
- Stats: Generative AI can reduce design production time by up to 70% (McKinsey, 2023).
3. Personalization Potential
- Brands can use generative art to tailor content for different demographics or customer segments.
Challenges of Generative Art Integration
1. Creative Authenticity
- Critics argue that AI-generated art lacks the emotional depth of human creativity.
2. Ethical Concerns
- Copyright issues arise when datasets use existing artworks without permission.
- Transparency about AI’s role in content creation can affect audience trust.
3. Technical Learning Curve
- Integrating generative AI into workflows requires technical knowledge, which may not be accessible to all teams.
Statistical Insights into Generative Art Adoption
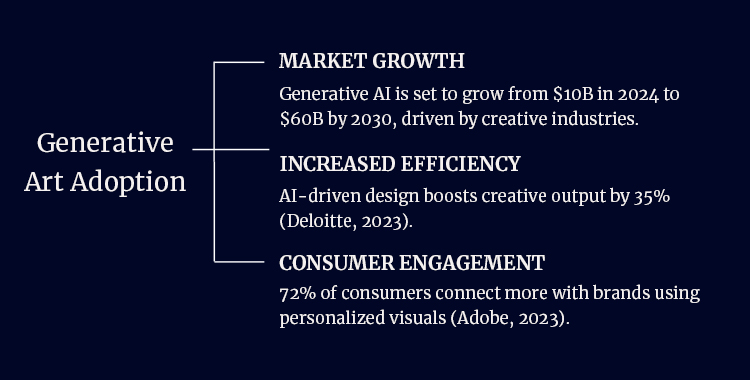
- Market growth: The generative AI market is expected to grow from $10 billion in 2024 to $60 billion by 2030, driven largely by creative industries (Allied Market Research, 2024).
- Increased efficiency: Companies using AI for design report a 35% improvement in creative output (Deloitte, 2023).
- Consumer engagement: 72% of customers feel more connected to brands that use personalized, creative visuals (Adobe, 2023).
Applications of Generative Art Across Fields
1. Advertising
- Generative art enables brands to produce adaptive campaigns tailored to specific audiences, locations, or platforms.
2. Social Media
- AI-generated content drives engagement by offering dynamic and visually compelling posts.
3. Traditional and Digital Art
- Artists collaborate with AI to explore new styles, push boundaries, and create pieces that challenge the norm.
4. E-Commerce and Product Design
- Brands use generative art for custom product designs, enhancing customer interaction and satisfaction.
Projections: Generative Art in the Future

1. Integration with AR/VR
Generative art will power immersive experiences in augmented and virtual reality, redefining digital interactions.
2. Co-Creation Models
AI will act as a collaborator, not a replacement, allowing humans to guide generative processes for tailored outputs.
3. Sustainability and Efficiency
AI systems will optimize designs to minimize waste, aligning with sustainability goals.
How Brands Can Leverage Generative Art
Experimentation and Prototyping
- Use AI to rapidly prototype and test ideas before finalizing designs.
Content Personalization
- Tailor visuals for specific audience segments based on data insights.
Brand Storytelling
- Integrate generative art into narratives that emphasize innovation and creativity.
The Canvas of Tomorrow
Generative art is not merely a tool but a paradigm shift in how brands approach creativity. By integrating AI-driven designs into ads, social media, and beyond, companies can unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and personalization.
However, the success of generative art depends on ethical implementation, strategic integration, and a balance between human intuition and AI efficiency.
Brands that embrace this technology now will position themselves as pioneers in a new era of marketing—where creativity is reimagined, and possibilities are infinite. For marketers, artists, and designers alike, the question isn’t whether generative art will shape the future, but how boldly they’ll wield this transformative tool.





